
Web Industries’ allocates capacity for COVID-19 diagnostic tests
Research and development work on the invention was led by professor Katarzyna Grabowska.

12th November 2019
Innovation in Textiles
|
Åódź
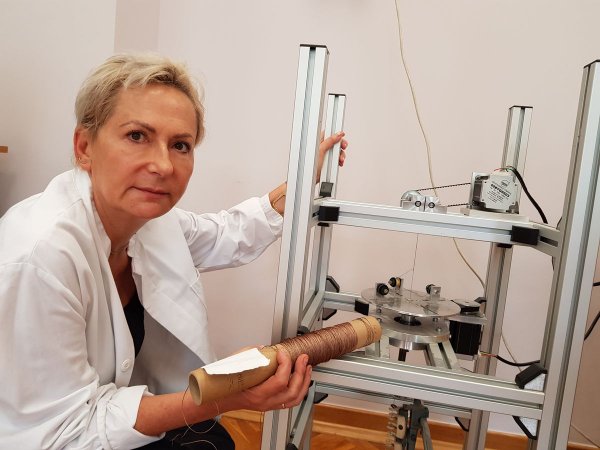

Professor Katarzyna Grabowska. © Åódź University of Technology
A group of researchers from Poland’s Åódź University of Technology (ÅUT) have developed a textile charger, which allows to charge phones, tablets, and other portable electronic devices using the power generated by their users’ physical activity.
Research and development work on the invention was led by professor Katarzyna Grabowska, the dean of the Faculty of Material Technologies and Textile Design at the ÅUT.
Monika Malinowska-Olszowy, PhD, the faculty’s vice dean, who is also a member of the research team that developed the textile charger, told Innovation in Textiles that the invention is based on the research on the structure and capacities of decorative and hybrid threads.
“The textile charger for mobile electronic devices is an inseparable part of the fabric or knitwear from which it is made, such as clothing,” she said. “It produces electricity on a continuous basis, allowing to power mobile electronic devices such as … smartphones, tablets or other devices. This invention replaces heavy, large batteries and power banks that often contain toxic substances. It is shock resistant and weatherproof.”
“The main purpose of this technology is to ensure its users with uninterrupted access to electricity to sustain the operations of their mobile devices. As a result, this will exclude various problematic processes related to frequent charging of mobile phones or tablets.”
The invention is already patented at Polish (PL 225484) and European (EP 3 021 454 A1) level.
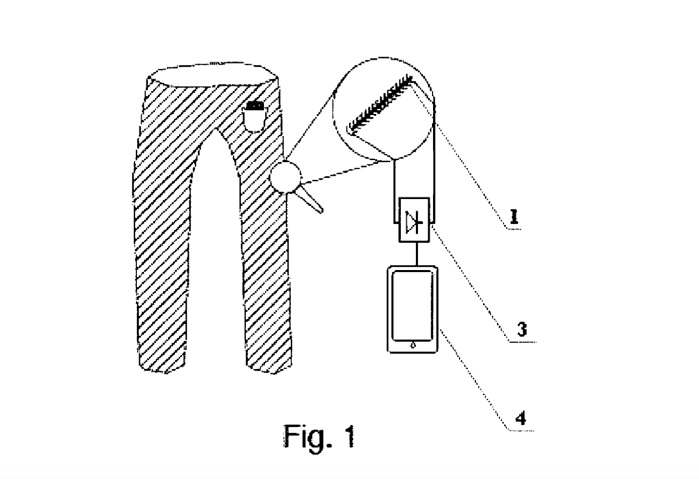
Image from patent application PL 225484. © Åódź University of Technology
“According to the invention, the textile charger for mobile electronic devices contains [a] thread for electro-magnetic induction, woven using any weaving or knitting technique into the fabric or cloth of an article of clothing worn by the user of the electronic device and located opposite the permanent magnet in another article of their clothing and performing shuttle movement in relation to the thread for electromagnetic induction,” the invention’s European patent application says. “Both ends of the thread for electromagnetic induction are linked via a cable to an electrical transducer, which in turn is connected via a cable to the powered electronic device.”
The textile charger’s electrical “transducer converts electrical current, inducted in the thread for electromagnetic induction as a result of the magnet’s movement in relation to the thread, to a form conforming to the requirements of the electronic device,” according to the patent application.
To finance a part of its activities, the research team has obtained a grant from the Polish Ministry of Science and Higher Education, allocated under the EU-funded Innovation Incubator 2.0 project. The funds will be used to promote the developed technology and allow the textile charger to be commercialised.
The Polish researchers are currently seeking an investor to initiate serial production of their invention. Asked whether the research team was planning to launch export sales of the textile charger, the vice dean said that this was planned “if an investor will be found.” The ongoing search for a financial partner is likely to be completed with success, as “there are no similar products on the market,” said Prof Malinowska-Olszowy. “We’re currently holding talks with a number of interested companies and funds, including ones from abroad,” according to the researcher.

Faculty of Material Technologies and Textile Design. © Åódź University of Technology
Over the past years, the ÅUT has solidified its position of one of the country’s leading academic research institutions focused on the development of innovative textile inventions. Some of the latest examples include textile clothing for premature infants that is to protect them against dehydration and ensure thermal stability through special layered textile systems, and a prototype textronics solution that allows the integration of muscle-stimulating electrodes within various types of clothing, such as underwear, wristbands and socks, and use it to treat patients with various diseases that require such stimulation, among others.
Åódź, which is Poland’s third largest city, has long served as the centre of the country’s textile industry. In 2015, the government announced plans to invest some PLN 400 million (EUR 94 million) to fund R&D activities by entities located in the city. As part of the Innotextile programme, the authorities are supporting the development of innovative textiles, such as hydrotextiles, geotextiles and agrotextiles, as well as their production by local manufacturers.

Business intelligence for the fibre, textiles and apparel industries: technologies, innovations, markets, investments, trade policy, sourcing, strategy...
Find out more