
Eleven green bottles...
Warp and weft combinations influence performance properties.

11th November 2024
Innovation in Textiles
|
Adlington, United Kingdom
In the world of workwear, the structural weaves of fabrics play a crucial role in determining the durability, comfort and overall performance of garments.
Carrington Textiles explains that understanding these weaves is key to selecting the right textile for different applications, ensuring safety and comfort and maintaining the professional appearance of work uniforms.
The fabric weave is the process of interlacing lengthwise warp yarns and crosswise weft yarns in fabrics. Tighter weaves create stronger, more resilient fabrics, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. Workwear fabrics like Carrington’s bestselling Teredo are designed to handle tough environments while maintaining their structure over time.
Different weave patterns also produce unique textures, from smooth and refined to rugged and structured, so the choice of weave affects how a garment feels to the touch and how it interacts with other layers of clothing.
Looser weaves allow greater airflow, making them suitable for warmer climates and physically demanding environments. Carrington’s Spartan HT Flex Lite military fabric, for example, balances breathability with durability, making it ideal for high-activity while providing high levels of performance.
Fabrics with satin weaves have a glossy finish, while plain weave fabrics offer a more matt appearance. Carrington’s Flamestat Satin family uses satin weaves to provide a sleek look, paired with flame-retardant properties for environments where safety and presentation are both key.
The density of the weave contributes to the fabric’s weight, influencing its drape and comfort. A lighter weave is often chosen for garments that require ease of movement, while heavier weaves provide additional warmth and protection in colder conditions.
The following seven weaves are the most commonly used in Carrington’s fabrics.
1. Plain weave is a simple, classic weave with threads crossing alternately over each other to produce strong, durable and tightly woven fabrics, providing a balanced texture. Such fabrics are ideal for office uniforms, shirts and industrial protective clothing.
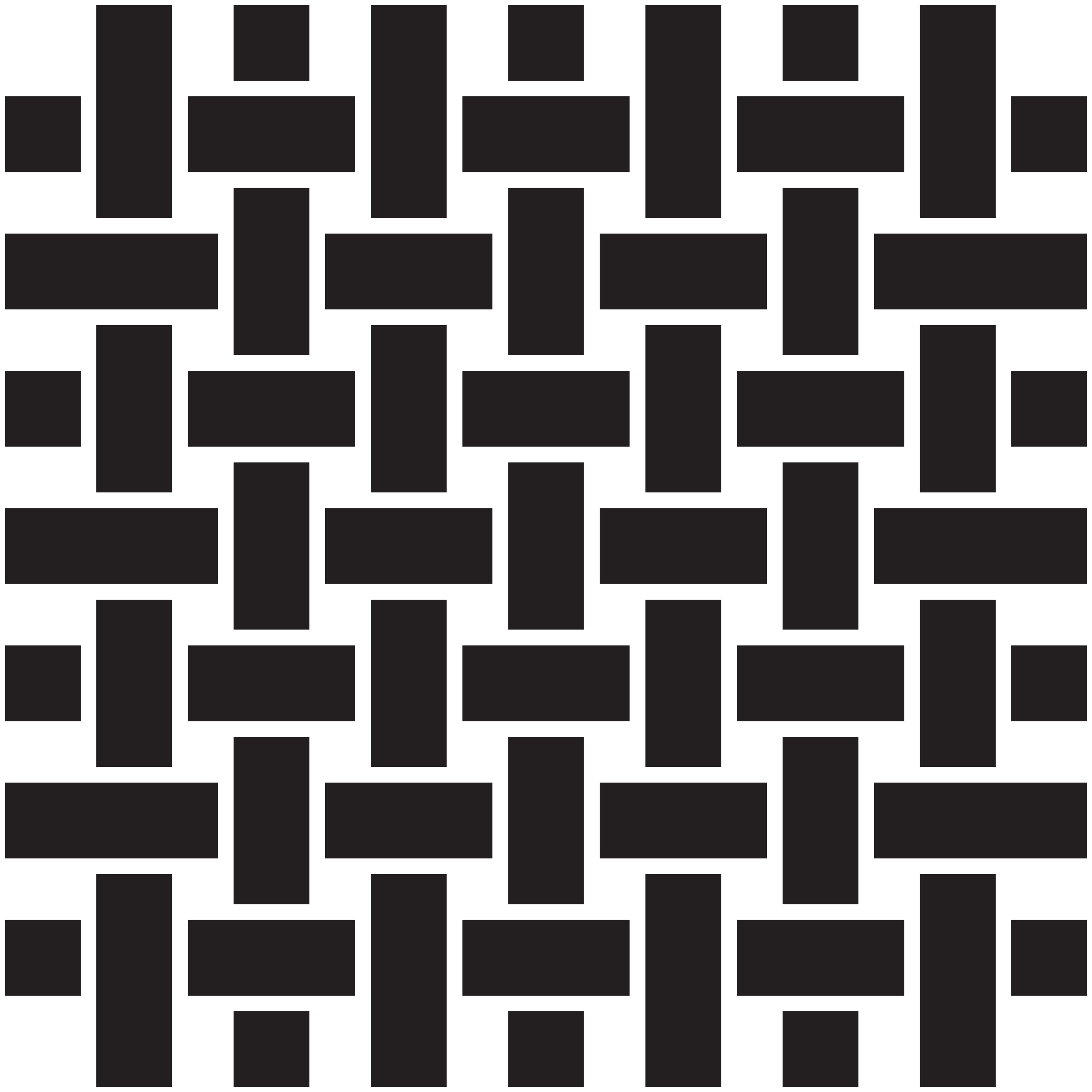
2. Canvas weave is a variation of the plain weave, using thicker yarns for enhanced robustness. This weave is known for its exceptional abrasion resistance, making it perfect for heavy-duty workwear like overalls, jackets and construction uniforms.
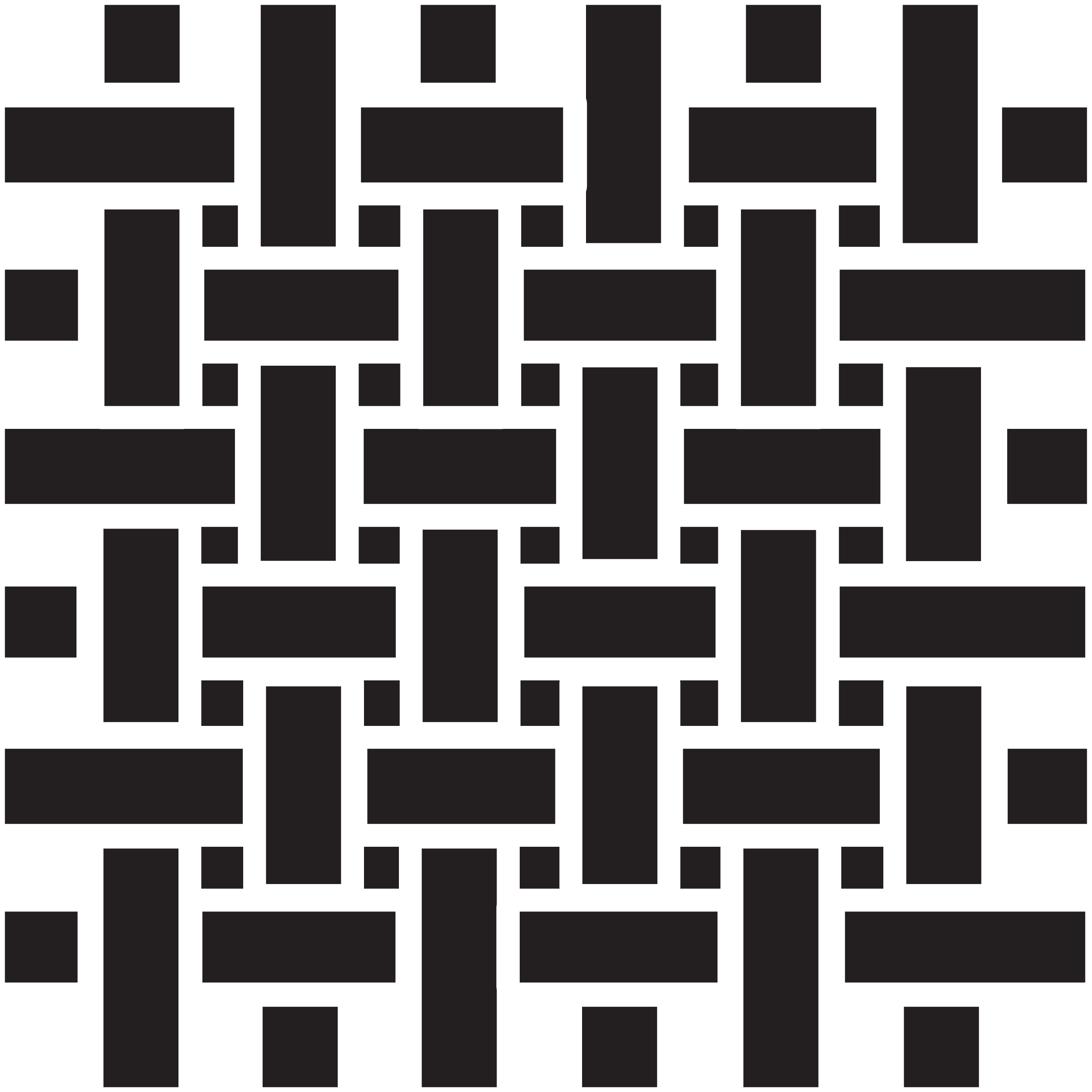
3. In S twill weaves, diagonal yarns slant from top left to bottom right, creating a distinctive texture. These fabrics offer flexibility, durability and resistance to wrinkles, maintaining a polished look and are used in mechanic uniforms, work trousers and sturdy shirts.
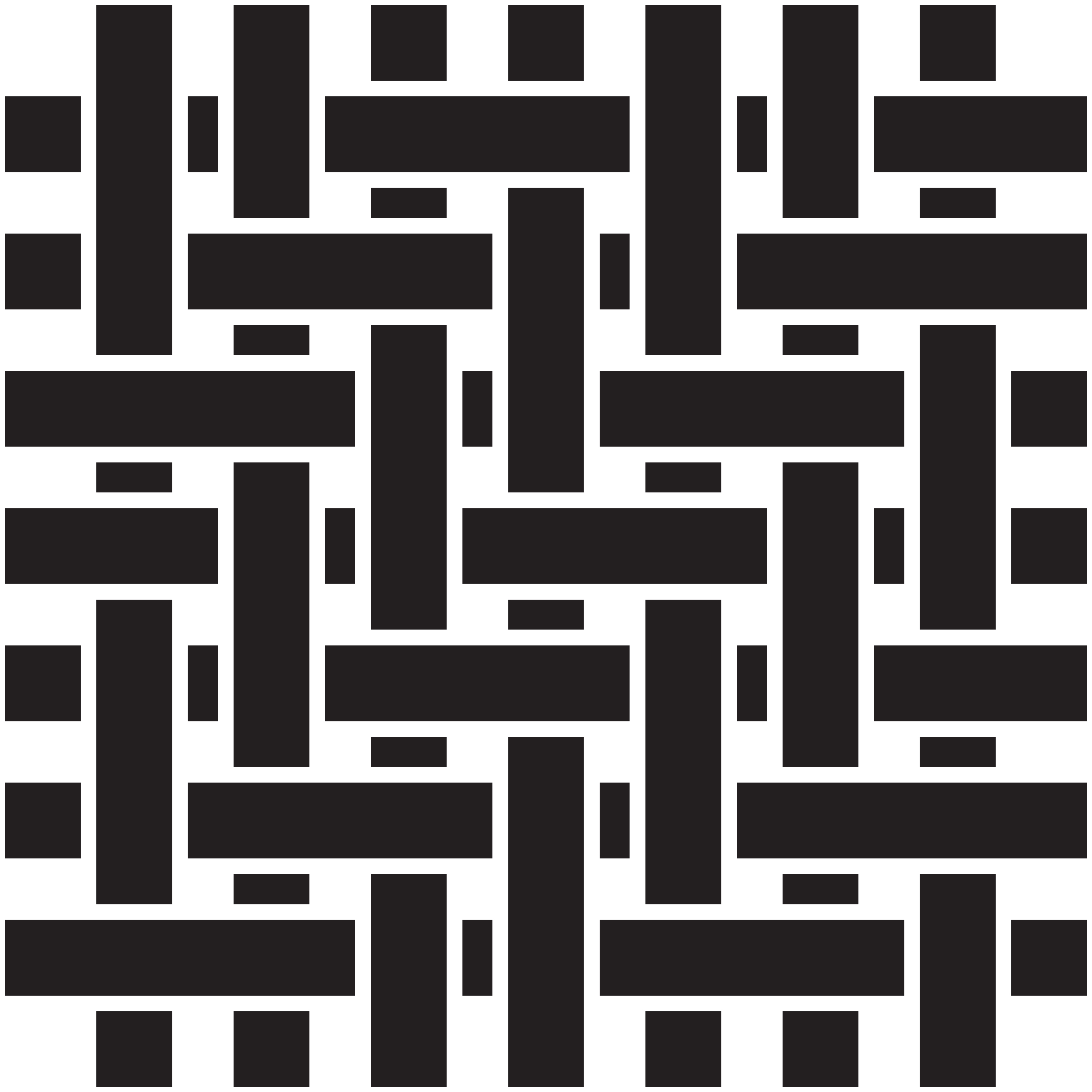
4. Similar to S twill, Z twill has diagonal lines running from top right to bottom left for a different visual appeal, often used in security uniforms, corporate wear and the hospitality sector.
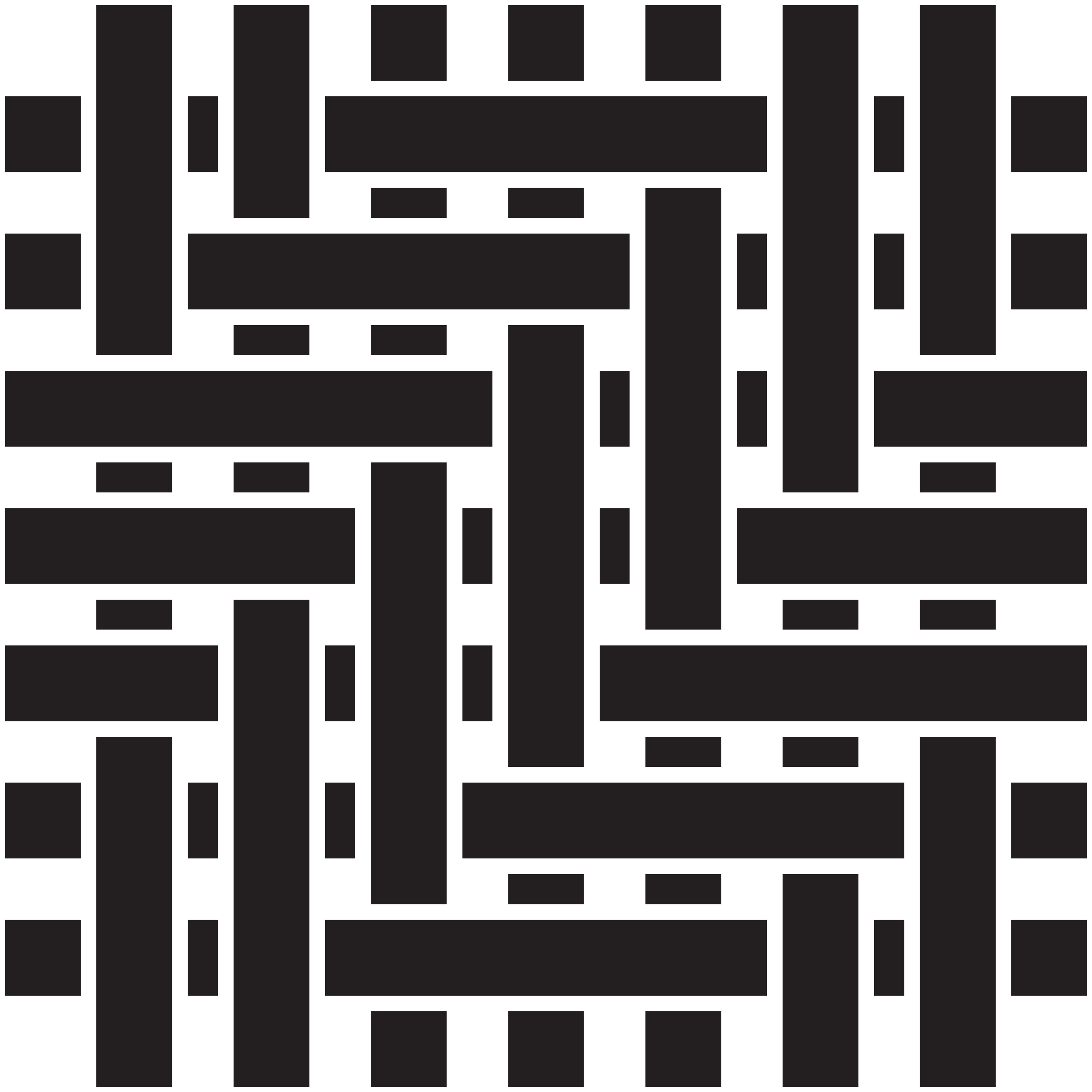

5. In broken twill the diagonal direction of yarns alternates, breaking the lines. These fabrics minimise fabric twisting while offering a unique texture and visual effect for use in delivery uniforms, fieldwork attire and high-mobility roles.
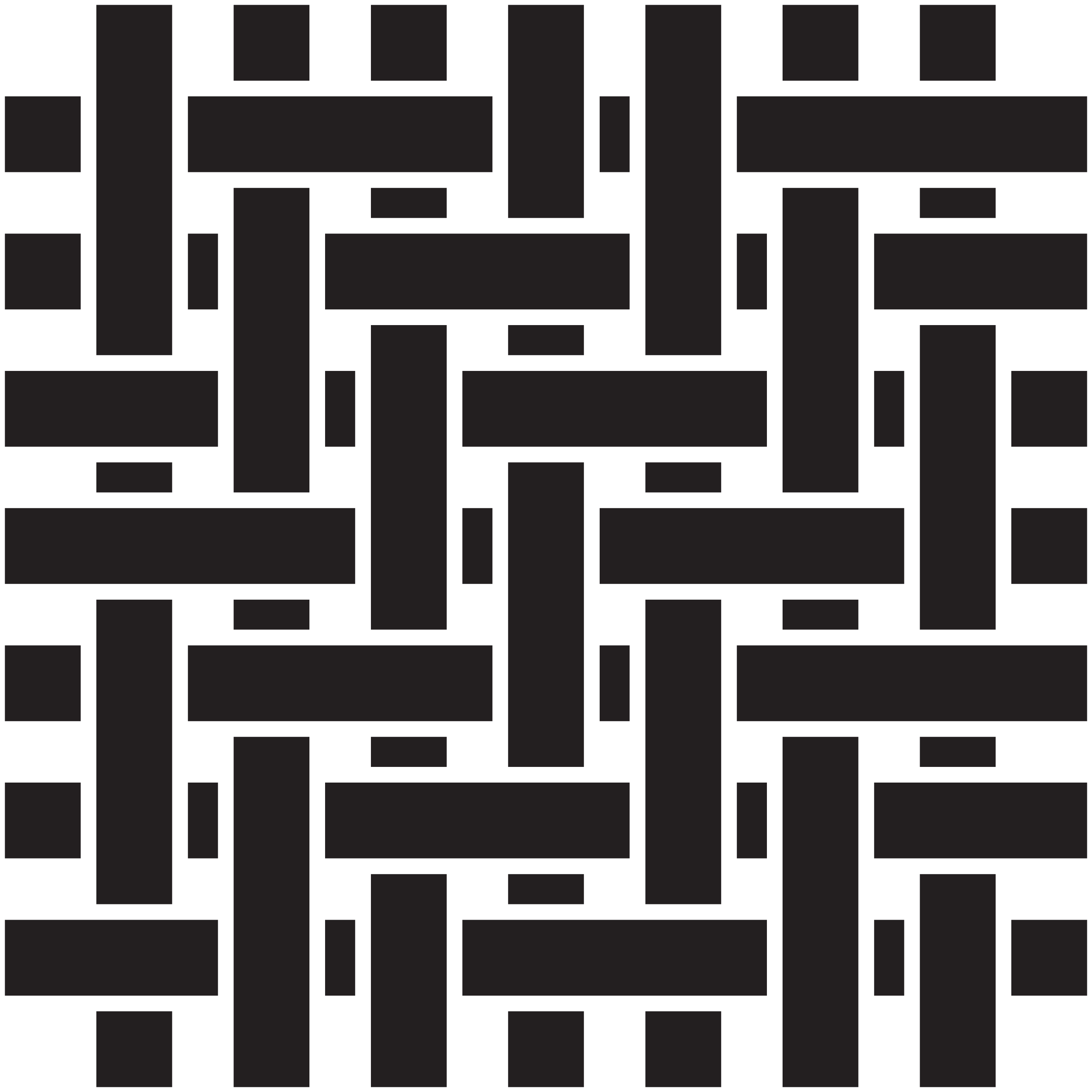
6. Panama weave is an enhanced version of plain weave where yarns are grouped together for a balanced finish. The weave uses two ends weaving as one, and either two picks weaving as one for a full Panama or one pick for a Half Panama. Fabrics with this structure are breathable and durable, with a subtle texture that makes them suitable for lightweight yet sturdy uniforms for the maintenance, hospitality and service industries.
7. Satin weaves are characterised by long floats of warp or weft yarns, creating a smooth and glossy surface with fewer interlocking points, resulting in enhanced drape. They are luxurious in appearance but less durable and used in high-end hospitality uniforms, ceremonial dress and specialised corporate wear.

Business intelligence for the fibre, textiles and apparel industries: technologies, innovations, markets, investments, trade policy, sourcing, strategy...
Find out more